As cyber threats continue to become more sophisticated, businesses and organisations need to be prepared for what the future of cyber security holds. With that in mind, this article will discuss 10 predictions for cyber security in 2024 and how businesses can best prepare themselves. From increased regulations and compliance standards to new technologies and strategies, it is important to be aware of the potential changes that may come in the next few years.
1. Targeted Ransomware
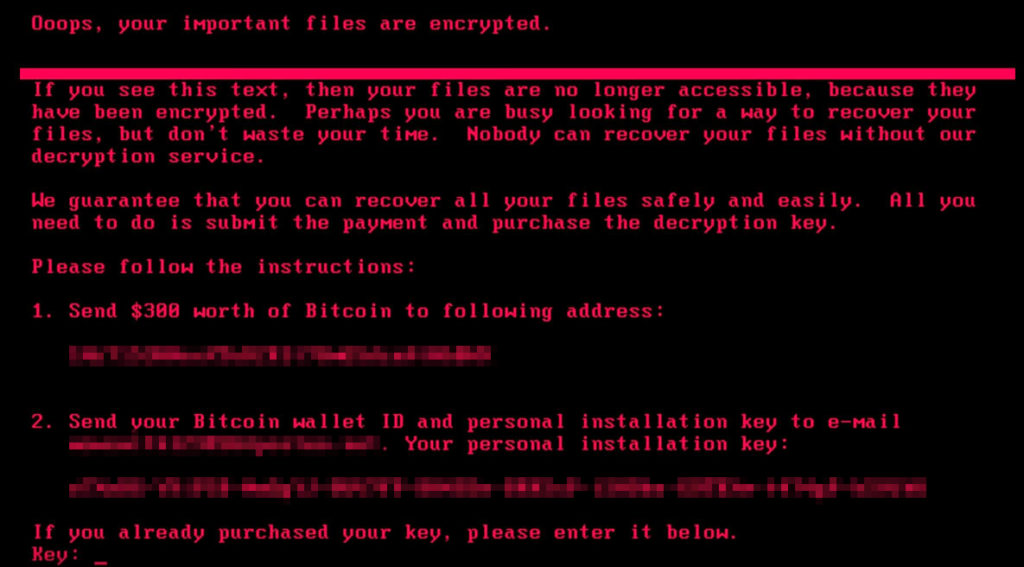
As cybercrime continues to evolve, so does the sophistication of attacks. In particular, the rise in targeted ransomware is expected to be the latest threat to cyber security in 2024. This type of attack is especially concerning because it allows malicious actors to take control of an entire system or network and effectively hold it hostage until a ransom is paid.
Targeted ransomware uses advanced techniques such as social engineering, password cracking, and other methods to gain access to corporate networks. Once inside, attackers can encrypt important files or systems and demand payment for their release. What makes this form of attack particularly dangerous is that organisations may not realize they have been compromised until it's too late – at which point they are faced with a difficult choice: comply with demands or risk losing their data permanently.
Recently large-scale, multi-national, corporate organisations and the public sector have been targets for this type of attacks. For organisations, downtime means lost revenue, while in the public sector the risk of data loss and government threat looms largest.
Consider taking a look at our recommendations for building a cyber security plan for 2024 to ensure that your strategy puts effective measures in place to protect against the most basic entry points for ransomware attacks.
2. State-sponsored Cyber Warfare
In 2022 we saw a massive rise in state-sponsored cyber-attacks, following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Cyber warfare quickly took hold and became a vital weapon in the arsenal of all of the countries involved. Reports from leading industry experts are predicting that this rise will only continue throughout 2024, with governments around the world continuing to expand their capabilities when it comes to launching, and defending, sophisticated, large-scale attacks against foreign and domestic targets.
While state-sponsored cyber-attacks are mostly about geopolitical spying, it is also used as a weapon to gain user credentials, and personal data, attack vital supply chains and gain industrial secrets held by another country.
While your organisation may not be the target of an entire state, you should still consider the possibility of attacks from foreign locations, and prepare accordingly. As we have seen cyber warfare can be every bit as vital as battlefield warfare, and we can expect to see defence budgets in these areas climb exponentially throughout the year.
3. Multi-factor authentication attacks
If you read our article on how to protect your data online back in October, you’ll already be aware of multi-factor authentication (MFA). It is an ever more essential security measure that should be used by organisations to allow their users to gain access to resources such as VPNs, email, and their accounts. It involves the use of two or more pieces of evidence, such as passwords and verification codes, to prove that a user is who they say they are. However, attackers have become increasingly adept at exploiting MFA vulnerabilities for their own financial gain.
Cybercriminals can use phishing schemes to obtain login credentials through emails sent to unsuspecting victims. Once these details are obtained, the attacker can then use social engineering techniques like call forwarding or account takeover scams to access additional information and bypass multi-factor authentication protocols. Additionally, attackers may also use malware programs that target weak MFA implementations in order to gain access to sensitive data stored in cloud databases.
So, while you there are many ways to protect against MFA attacks, including regular training, email filtering, virus and malware scanners, there is one element that cannot be protected against: Multi-factor authentication fatigue.
What is Multi-factor Authentication Fatigue?
Unfortunately, with the ever-growing need for MFA, many users are experiencing a phenomenon known as multi-factor authentication fatigue.
Multi-factor authentication fatigue occurs when users become overwhelmed by the number of passwords and codes, they have to remember in order to access their accounts or services, leading them to unintentionally ignore or skip these steps. Users may have several different accounts that require them to enter their username or password multiple times before they can complete the login process. It’s often difficult to keep track of all these credentials, which can lead to frustration and burnout with MFA systems. Additionally, if users forget one of their passwords or codes, they may spend hours trying to reset it without success.
How to Protect Against MFA Fatigue?
In order to best protect against MFA fatigue, organisations should take the following measures:
First and foremost, organisations should strive for user-friendliness when setting up an MFA system. Requiring too many steps or making users remember complex passwords can create confusion and frustration that leads to fatigue. Additionally, consider using biometric authentication instead of relying solely on passwords; this eliminates the need for typing out long strings of numbers and letters and makes logging in much easier. You can also make use of AI and ML-enabled solutions which track user behaviour patterns and alert you to suspicious activity before it takes place.
Vitally, though, training and educating your organisation’s employees is the first step to protecting against these specific types of attacks. Overall, this should just be one element of a wider cyber security strategy that you implement and undertake to protect your systems, networks, and services.

4. Zero trust
Zero trust is an increasingly popular security framework that seeks to protect organisations from cyber threats. In the past, individuals and organisations had to rely on firewalls and other perimeter-based security measures to keep out malicious actors. However, zero trust represents a shift in thinking by eliminating the traditional network perimeter, instead focusing on verifying identity of users before granting access.
The core principle of zero trust is to never blindly trust anyone or anything - even those already inside your network's perimeter. This means that all users and devices must be authenticated via multi-factor authentication procedures such as biometrics, tokens or passwords. Furthermore, any requests for data must be authorized based on roles and policies defined by the organization’s security team. By taking this approach, zero trust can help organizations reduce their exposure to cyber attacks by preventing malicious actors from exploiting vulnerable points in their systems.
While zero trust is certainly not the silver bullet of cyber security, it should be part of a strategy for cyber security in 2024 that thrives to authenticate every user within a cloud network and infrastructure.
5. Deepfake Technology
On the topic of biometric authentication data, deepfake technology will become an increasing headache for organisations throughout 2024.
Deepfakes are digital media such as videos and images that have been manipulated to appear real. These manipulations can be used for malicious purposes like impersonating someone else, spreading false information and damaging an individual's or company's reputation. Deepfakes can also be used to gain access to confidential data or infiltrate computer systems, making them difficult to detect by traditional security measures.
Deepfake technology is not only becoming more sophisticated but more available as well. It is now easier than ever for anyone with basic knowledge of computer programming to create convincing deepfakes using readily accessible software tools and tutorials available online. This means that it is increasingly difficult for organisations to protect themselves from these threats.
The cyber security threat of deepfakes does not come from the technology, but society’s impulse to believe what they see on the surface, and as such, the fakes do not need to be all that advanced to be successful in their mission.

Legislation is slowly coming into force to protect organisations and individuals against deepfake activity, but unfortunately, legislation doesn’t go far enough to make you invulnerable. Fortunately, however, more and more cyber security companies are creating improved detection algorithms that analyse the distortions created during the faking process.
Here are some ways you and your staff can look out for deepfake material:
- Movement that is twitchy or jolting
- Lighting changes from frame to frame
- Skin tones that appear to change throughout the video
- Unusual eye blinking or no blinking at all
- Speech synced badly to lip movement
- Artifacts within the video itself
As deepfakes advance, these manual methods will become more and more unlikely to work, and there will be further requirements for AI methods to protect against them.
6. Working from home
Working from home has become increasingly popular in recent years, with more and more businesses allowing their employees to do so. With the shift in working environment, however, comes a heightened risk of cyber security threats.
Cyber criminals have taken advantage of the new trend and are now launching attacks on remote workers. Those who work from home may be exposed to malware or ransomware if they're not careful about their internet activities. Furthermore, unsecured Wi-Fi networks can lead to data leakage as hackers can easily intercept files or gain access to confidential information. Additionally, increased use of personal devices for work purposes may also create risks as these devices may lack necessary security settings or software updates.
In order to protect against cyber security threats when working from home, employers should advise their staff members on proper cybersecurity practices such as using secure passwords and avoiding suspicious links or emails, as well as making use of secure networks and company-provided VPNs.
7. Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security
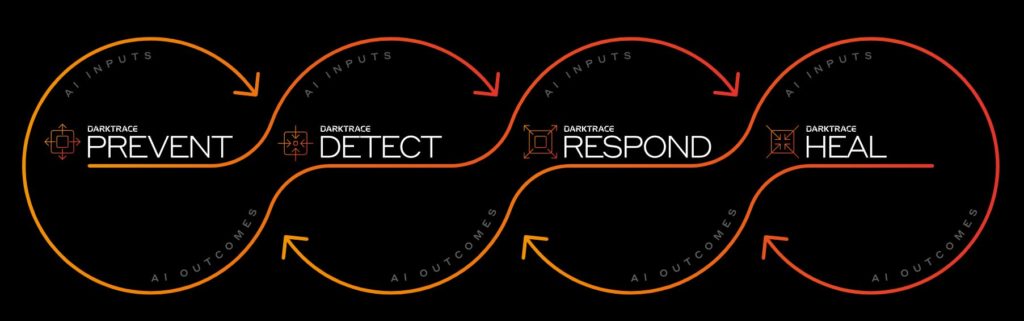
As you may have seen back in December, we posted an article about Darktrace, a breakthrough cyber security service that utilises AI and machine learning to help organisations develop their security strategy, analyse user behaviour and malicious threats, as well as an upcoming service that will return a network to it's previous state in the event of a successful cyber-attack.
As we just discussed in the Deepfake section of this article, we expect to see more and more solutions developed throughout this year, to tackle the ever-growing issues within cyber security. As the types of attack get more varied and organisations' networks and systems scale, it becomes all the more difficult to manually monitor the potential attack surface.
AI algorithms are increasingly being used to detect, investigate and respond to potential cyber-attacks in order to protect networks and data from malicious activities. Using cognitive computing capabilities such as machine learning and natural language processing, AI can detect suspicious patterns of behaviour, analyse large amounts of data quickly and accurately, process encrypted communications and help identify potential vulnerabilities in IT systems.
The use of AI not only helps increase the accuracy of cyber security solutions but also reduces operational costs associated with manual investigations. By automating repetitive tasks that require extensive review by human experts, organizations can quickly detect anomalies in user behaviour or system activity that might indicate a threat. Additionally, AI-driven solutions can predict trends earlier than traditional methods allowing for faster response times when it comes to preventing an attack.
While it may not be affordable for everyone, if your organisation is serious about its cyber security in 2024, an AI solution should be in your thoughts.
8. Secure Access Service Edge
SASE is a cloud architecture model that provides organisations with unified networking and security solutions. It combines multiple services such as VPNs, firewalls, zero trust networks, SD-WANs, DDoS protection and more into one single service.
SASE works by securely connecting users to corporate applications and data from anywhere in the world. Security features like encryption and authentication can be used to protect data in transit or at rest. Additionally, users are authenticated using multi-factor authentication processes which ensures only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. As a result of this secure connection between users and corporate resources, organisations can enjoy improved productivity while keeping their operations safe from cyber threats.
Throughout 2024 we believe SASE will see a big push as organisations seek to minimise the distance between their network and the end user, improving security of their data and improving their network performance.
9. Training
One of the core fundamentals of cyber security in 2024 should be your employee training strategy. Your employees weren't taught the dark art of monitoring for cyber-attacks during their school years, and unless some of them have gone out of their way to do so, it's unlikely many will have any knowledge on the topic. That's why, this year, it is vital you consider advancing your cyber security training internally, in addition to implementing the practical solutions.
Phishing will continue to be the lowest sophistication attack that is carried out on organisations throughout the year, and yet, many will still fall foul of such a simple attack, potentially giving way to large data breaches and ransomware takeovers.
Consider utilising training platforms and AI to customise training effectively on a per user level, and reward interest and success for those who help to protect your organisation's security interests. Training should not be seen as an optional extra, but a necessity for your success. Investment in upskilling is well worthwhile when compared to not only the financial losses of data breaches, but also in reputational damage caused by public knowledge of such events.

10. Cyber Insurance
With the increase in cyber attacks and the types of malicious activity taking place, it's understandable that cyber insurance has fallen foul of price hikes, just as much as other commodities. In Q1 of 2022, cyber insurances premiums increased by 28% compared to Q4 of 2021. With the increased financial and reputational risks of cyber attacks it's no real surprise.
We expect that throughout this year cyber insurance will not only become more expensive, but also more difficult to obtain, as underwriters implement strict requirements for MFA and specific technologies. Once upon a time, cyber insurance required you to fill out a 2-page questionnaire, but now we see requirements for full audits and 12 pages of questions that you'll be needed to answer.
We also expect to see more companies requiring their vendors to also have cyber security insurance in order to work with them. Throughout 2024 the demand for cyber insurance will continue to trend upwards, alongside their premiums, and the number of requirements to obtain it.
Summary
Cyber security in 2024 is expected to continue to require more investment, more awareness, and more intelligence than ever before. Not only do organisations need to be aware of low-level phishing scams, multi-factor authentication, and general workplace knowledge and culture, but they also need to be aware of the geopolitical impact on elements such as insurance and supply chain.
Though the challenges associated with cyber security may seem daunting, there are many proactive steps that businesses and individuals can take to increase their level of protection from cyber threats. It is imperative that organisations stay current on the latest trends in cyber security technologies and best practices for staying safe online.
If you require assistance in developing or implementing your cyber security strategy, why not get in touch with our friendly team who'll be able to give you a helping hand,