Phishing attacks: they're one of the biggest cyber security topics in business. If you spend any time online, chances are you’ve encountered phishing, or even been a victim of it. But don’t worry - there are plenty of steps you can take to protect yourself and your information from those pesky kids. In this article, we will provide an overview of how to prevent phishing and keep your personal data secure.
What is Phishing?
Welcome to the world of phishing! Have you ever received an email from what appears to be a colleague’s email address, containing a link to click on, only to find out that it wasn't from your colleague after all? It looks legit enough, the email address includes what looks like your business name and the screen the link takes you to looks exactly like your Microsoft login page.
That's phishing in a nutshell. Phishing is simply a low-sophistication cyber attack that aims to gain your private data, which will give them the credentials they need to access other sensitive information that belongs to you, your colleagues, or your business.
Phishing is one of the most common cyber-attacks out there, and prevention is key. Fortunately, there are a variety of measures you can take to protect your business and colleagues from phishing scams.
Types of Phishing Attacks
Phishing is an increasingly common form of cyber-attack, and it remains a major threat to businesses. It is a type of social engineering that involves perpetrators sending fraudulent emails or messages in an attempt to steal sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card details, and more.
There are several types of phishing attacks, each with its own methods and goals. Understanding the different types of phishing attacks can help you prepare your organisation for the dangers they pose, so let’s take a look at the most common types of phishing attacks that you should be on the lookout for:
1. Email Phishing
The most common form of phishing attack and the most commonly fallen for attack. In a typical email phishing attack, hackers will use social engineering tactics such as creating fake websites or emails that look like they come from reputable sources, in order to get victims to click malicious links or enter private credentials into fraudulent forms. Attackers may also use emails with attachments containing malware which can allow them access to devices and networks, allowing them to steal sensitive data or disrupt services.
It is essential for businesses and users alike to stay vigilant when it comes to email phishing attacks, as the consequences can be severe.
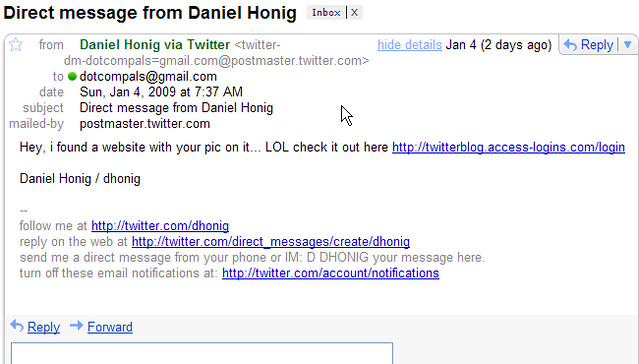
2. Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is email phishing’s younger, but more intelligent brother.
Unlike traditional phishing attacks where emails are sent to large amounts of people randomly, spear phishing is highly targeted and personalised. Cybercriminals conduct research on the victims by collecting personal details from various sources then use them in their messages, making it more difficult for potential victims to recognise the scam.
These types of attack will often use some or all of the following information in their tactics:
- Their name
- Employer
- Job title
- Specific business email addresses
- Other specific information about their job role.
Additionally, the attackers often pretend to be from a trusted organisation like banks or government agencies which can further deceive unsuspecting users into disclosing confidential information.
3. Whaling & CEO Fraud
When it comes to business, a common phishing attack comes in the form of “Whaling” or CEO fraud. Malicious actors make use of social media and your own business website and listing information to gain the required information about the managing directors or CEO. This is then used to impersonate these people using similar email addresses, before sending an attack that asks unsuspecting employees to carry out financial transactions.
A quick and easy way to identify a whaling attack is to look out for a “manager” who prefaces the email with the fact that they are extremely busy and can’t carry out said transaction themselves.

4. Smishing and Vishing
Smishing
Smishing, or SMS phishing, is an increasingly common form of cybercrime. It is a type of phishing attack that uses SMS messages as the delivery method for malicious content. The goal of a smishing attack is to get the recipient to click on a link or respond with sensitive information.
Unlike traditional phishing attacks, which use email as the delivery method, smishing involves sending fake text messages from seemingly trustworthy sources such as banks or companies. These messages are designed to trick the recipient into clicking on malicious links, downloading malware, or divulging confidential data such as bank account numbers and passwords. Smishers often make their messages appear urgent in order to convince recipients to act quickly without thinking twice about it.
Vishing
Vishing, or voice phishing, is a type of attack often carried out through phone calls where the attacker creates a sense of urgency that encourages the victim to perform an action that they believe is in their best interest. This type of attack will often increase in frequency around the time of common deadlines such as tax returns.
5. Angler Phishing
One of the newest types of attack, angler phishing utilises information that users voluntarily put out on to their social media accounts in order to create highly targeted attacks that make the victim believe there is no possible way it can be a scam. They then use fake URLs, cloned websites, and tweets or instant messages to create a high sense of urgency.
This attack is common on an organisations social media posts where customers may be responding about complaints. Scammers will often use a fake profile that looks like your organisation and will request the customers' personal information.
Prevention Tactics
There are many ways a business can protect themselves against phishing scams. From improved security measures to employee training, businesses have the capability to prevent phishing before it becomes an issue. Here are a few ways your business can take action:
1. Configure your network appropriately
You should ensure that IT infrastructure including user accounts are configured using the principle of "least privilege", meaning you give the lowest amount of access rights possible for an employee's role within the organisation. This in turn places limitations on the impact of any successful phishing attack, by limiting the areas and sensitive data a malicious user can gain access to.
Also consider making use of cyber security standards such as two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts that are used to access sensitive data or networks. This makes phishing attacks much less successful, even in the event that they gain password data. Take a look at our articles about How to Protect Your Data Online and Build a Cyber Security Plan in 2023 for more information on how you can best prepare.
2. Know how to identify phishing scams
Most phishing attacks will have similar traits that you can identify within a few seconds. Take time to familiarise yourself and your employees on the common signs:
- Look for illegitimate information - check email address spellings, phone numbers, poor grammar, incorrect branding etc.
- Shortened links or incorrect links - hover over any link in the email and check the bottom left side of your browser to see where the link is going to take you to. If you don't recognise the URL, don't click on the link.
- Abnormal requests - if you suddenly receive a request from a colleague you wouldn't normally, consider contacting them using an alternative contact method to discuss its legitimacy.
- Be wary of shared drive links and password protected files - a lot of phishing scams will point users to fake shared drives where they are requested to enter their login details, or alternatively, to access password protected documents where they also need to enter a password.
- Caller or SMS sender number - look out for the phone number on a caller or SMS. It may be marked as spam or be received from an unusual location.
3. If in doubt, delete.
If you have any feelings of doubt about an email, you should delete it or send it to your organisations' IT security department.
4. Regular employee training
The most effective way to prevent successful phishing attacks against your business, is to simply teach your employees what to look out for and how to respond to an attack. By teaching your employees how they can identify common phishing scams, the chances of low-sophistication attacks being successful will be dramatically reduced, and with the appropriate cyber security plan and infrastructure, even a successful attack will gain little sensitive data.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Business
With the number of opportunist phishing scammers increasing by the day, it's never been more important to be aware of the signs and understand how to identify a malicious user. While they are extremely basic attacks, they are one of the most successfully carried out forms of cyber attack in the modern age.
If you want to discuss a cyber security plan for your organisation or to implement cyber security infrastructure why not get in touch with us today and talk to one of our experts.